
An AMC (Airborne Molecular Contamination) Cleanroom is a controlled environment specifically designed to minimize molecular contaminants such as acids, bases, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and condensable particles. Unlike traditional cleanrooms that focus on particulate contamination (e.g., dust and microbes), AMC cleanrooms control chemical contaminants that can impact sensitive manufacturing processes.
AMC cleanrooms require specialized air filtration systems (e.g., activated carbon, chemisorption filters) and strict material controls to prevent contamination from chemicals released by humans, equipment, or building materials.
Key Features of an AMC Cleanroom
- Advanced Filtration: Chemical filters (e.g., activated carbon, potassium permanganate) alongside HEPA/ULPA filters.
- Strict Material Control: Only low-emission materials are allowed inside.
- Continuous Monitoring: AMC sensors track contamination levels in real time.
- Isolated Airflow Designs: Prevents cross-contamination from external sources.
What industries may require it?
- Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology
- Aerospace & Optics
- Solar Panel & Battery Manufacturing
- Food & Beverage Processing
- Medical Device Manufacturing
Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing
- Why? Even trace amounts of airborne chemicals can damage microchips, causing defects in wafers, photomasks, and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- AMC Concerns: Acids (HF, HCl, HNO₃), bases (NH₃), VOCs, and metals.
- Example: Wafer fabrication, photolithography, and LCD/OLED production.
Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology
- Why?Molecular contamination can alter drug formulations and compromise sterile conditions.
- AMC Concerns: VOCs, endotoxins, and reactive gases.
- Example: Drug manufacturing, vaccine production, and gene therapy labs.
Aerospace & Optics
- Why? AMC can degrade optical coatings, precision mirrors, and sensitive instruments.
- AMC Concerns: Acids, bases, and hydrocarbons.
- Example: Satellite lens fabrication and precision optical instruments.
Solar Panel & Battery Manufacturing
- Why? AMCs can affect the efficiency and lifespan of solar cells and lithium-ion batteries.
- AMC Concerns: Metallic contaminants and VOCs.
- Example: Thin-film solar cell production.
Food & Beverage Processing
- Why? Certain airborne chemicals can alter taste, smell, and food safety.
- AMC Concerns: VOCs, microbiological contaminants.
- Example: Flavor production and dairy processing.
Medical Device Manufacturing
- Why? AMC contamination can impact sterilization and functionality.
- AMC Concerns: Organic vapors and acids.
- Example: Surgical implants and microfluidic devices.
Comparison Between Normal Cleanrooms & AMC Cleanrooms in the Semiconductor Industry
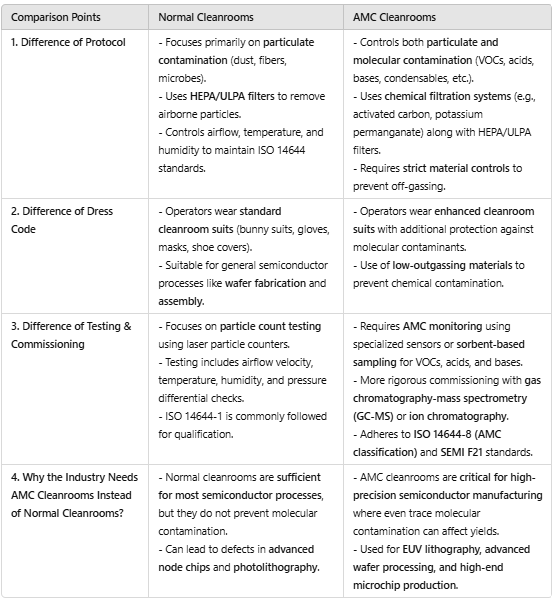
Conclusion
In the semiconductor industry, the choice between a normal cleanroom and an AMC cleanroom is determined by the level of contamination control required for specific manufacturing processes. While normal cleanrooms effectively manage particulate contamination, they fall short in preventing molecular contamination, which can significantly impact advanced semiconductor fabrication.
As the demand for smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient microchips grows, AMC cleanrooms have become a necessity rather than an option. Their ability to control airborne molecular contaminants ensures higher production yields, improved product reliability, and compliance with stringent industry standards like ISO 14644-8 and SEMI F21.
For semiconductor manufacturers aiming to remain competitive in the cutting-edge chip production sector, investing in AMC cleanroom technology is a strategic move. By implementing advanced filtration, strict material controls, and continuous monitoring, companies can safeguard their production processes against even the most microscopic threats, securing a future of innovation and excellence.
